Overview
Functional testing
- Functional testing consists of a sequence of tests that define entry values for an operation and observe if the result is what was expected.
- Functional tests may be run without any knowledge of the programming code that implements the operation; only its behavior is observed.
- The quantity of tests to be conducted in order to assure that an operation is correct may be virtually infinite.
- Functional testing may use techniques to reduce the number of necessary tests without losing coverage. The most useful techniques for accomplishing that goal are equivalence partitioning and limit value analysis, which are explained in the following subsections.
We need an easy way or special techniques that can select test cases intelligently from the pool of test-case, such that all test scenarios are covered. We use two techniques – Equivalence Partitioning & Boundary value analysis testing techniques to achieve this.
Boundary value analysis
Boundary testing is the process of testing between extreme ends or boundaries between partitions of the input values.
-
So these extreme ends like Start- End, Lower- Upper, Maximum-Minimum, Just Inside-Just Outside values are called boundary values and the testing is called “boundary testing”.
-
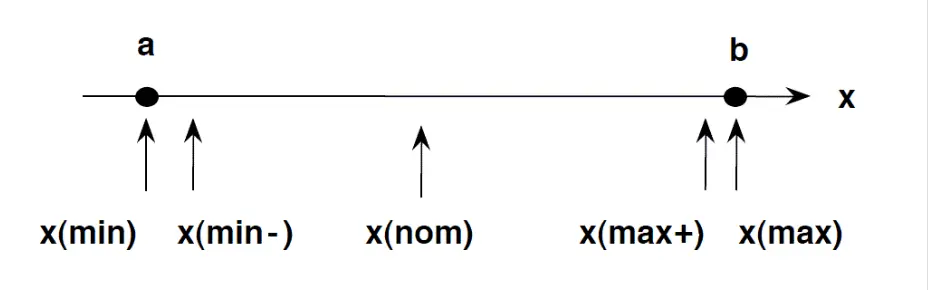
The basic idea in normal boundary value testing is to select input variable values at their:
- Minimum
- Just above the minimum
- A nominal value
- Just below the maximum
- Maximum
-
In Boundary Testing, Equivalence Class Partitioning plays a good role
-
Boundary Testing comes after the Equivalence Class Partitioning.
Equivalence partitioning
One of the principles of functional testing is the identification of equivalent situations.
Equivalence Partitioning or Equivalence Class Partitioning is type of black box testing technique which can be applied to all levels of software testing like unit, integration, system, etc. In this technique, input data units are divided into equivalent partitions that can be used to derive test cases which reduces time required for testing because of small number of test cases.
- It divides the input data of software into different equivalence data classes.
- You can apply this technique, where there is a range in the input field.
Why equivalence & boundary analysis testing
- This testing is used to reduce a very large number of test cases to manageable chunks.
- Very clear guidelines on determining test cases without compromising on the effectiveness of testing.
- Appropriate for calculation-intensive applications with a large number of variables/inputs
Example:
Equivalence and Boundary Value Let’s consider the behavior of Order Beer at the bar.
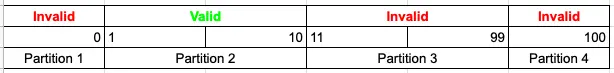
- Beer values 1 to 10 is considered valid. Order will be success.
- While value 11 to 99 are considered invalid for order.
Here is the test condition (Partitions):
- Any Number greater than 10 (let say 11) is considered invalid.
- Any Number less than 1 that is 0 or below, then it is considered invalid.
- Numbers 1 to 10 are considered valid
- Any 3 Digit Number say 100 is invalid.
We cannot test all the possible values because if done, the number of test cases will be more than 100. To address this problem, we use equivalence partitioning hypothesis where we divide the possible values of tickets into groups or sets as shown below where the system behavior can be considered the same.
The divided sets are called Equivalence Partitions or Equivalence Classes. Then we pick only one value from each partition for testing.
The hypothesis behind this technique is that if one condition/value in a partition passes all others will also pass. Likewise, if one condition in a partition fails, all other conditions in that partition will fail.
Summary:
- Boundary Analysis testing is used when practically it is impossible to test a large pool of test cases individually
- Two techniques – Boundary value analysis and equivalence partitioning testing techniques are used
- In Equivalence Partitioning, first, you divide a set of test condition into a partition that can be considered.
- In Boundary value analysis you then test boundaries between equivalence partitions
- Appropriate for calculation-intensive applications with variables that represent physical quantities
