Selecting the ideal JavaScript framework can be a daunting task, particularly when faced with an abundance of highly resourceful and capable options. To make an informed decision that caters to specific project requirements, it's crucial to possess a deep understanding of various critical aspects. In this article, we'll shed light on some of these essential points by conducting a comprehensive comparison of Angular, React, and Vue.
We’ve had our fair share of decision fatigue keeping up with new frameworks and choosing the right ones for the job. Our aim is to provide you with the necessary insights to determine the most suitable framework for your unique set of projects, helping you navigate the world of JavaScript frameworks with confidence.
A brief history of modern frontend development
Embarking on a journey through the history of frontend development, we first encounter jQuery, a groundbreaking JavaScript library released in 2006 that simplified the process of constructing interactive web applications. As jQuery gained traction, so did the concept of Single-Page Applications (SPAs), which enabled web apps to dynamically rewrite pages without the need for loading new pages entirely. This transformation in web development can be attributed to the ongoing refinement and structuring of front-end frameworks.
In 2010, AngularJS emerged as a pioneer in the world of frontend development, introducing revolutionary concepts such as two-way data binding, dependency injection, and modular architecture. These features facilitated the creation of maintainable, testable, and scalable applications for developers.
React, a brainchild of Facebook, was unveiled in 2013 and rapidly gained favor for its effective approach to building user interfaces with reusable components. Pioneering a new way to develop SPAs using the Virtual DOM, React enabled enhanced performance and more efficient updates. The framework's component-based architecture, unidirectional data flow, and thriving ecosystem made it an instant hit among developers.
Angular, first launched in 2016 as a comprehensive rewrite of AngularJS, assimilated the lessons learned from its precursor and further refined them. Providing a stable, built-in solution without sacrificing size or speed, Angular quickly carved out a niche in the development community.
In 2014, Evan You, who previously worked at Google and built applications with AngularJS, unveiled Vue, a progressive frontend framework explicitly tailored for crafting intricate user interfaces and views. Vue amalgamated the best aspects of React and Angular, presenting developers with a versatile, lightweight, and potent alternative.
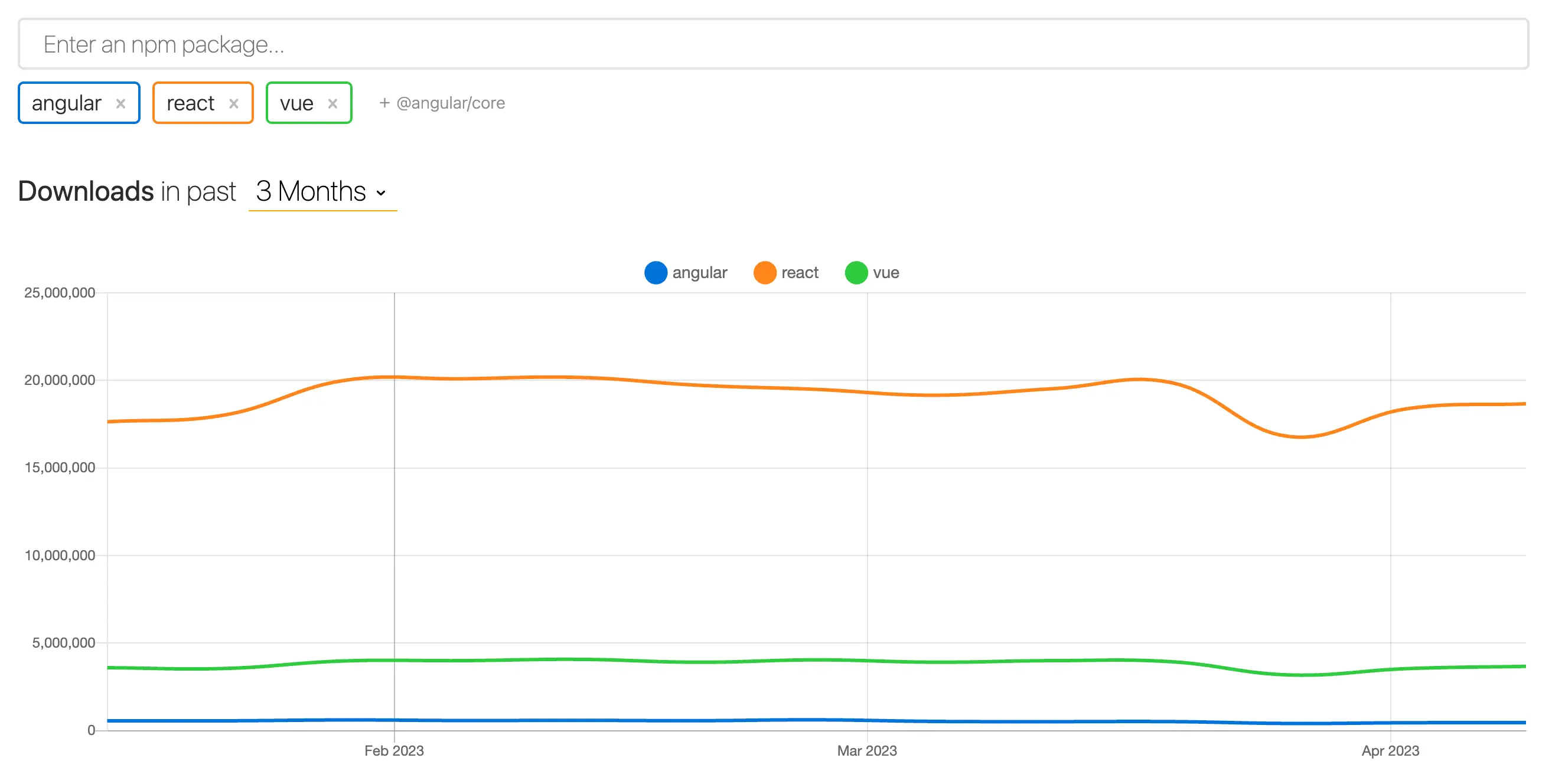
A quick comparison: React vs Angular vs Vue
As we embark on our journey through the world of React, Angular, and Vue, it's crucial to grasp the fundamental differences that set these popular JavaScript frameworks apart. Although they share common ground in building sophisticated and interactive web applications, each framework exhibits unique attributes that shape the developer experience. It’s useful to provide a quick comparison of React, Angular and Vue, laying the foundation for a more in-depth exploration of their technical nuances in the sections to follow.
| Feature | React | Angular | Vue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Release Year | 2013 | 2016 (Angular 2) | 2014 |
| Latest Version | 18.x | 15.x | 3.x |
| Popularity (GitHub Stars) | 200k+ | 87k+ | 210k+ |
| Developed By | Evan You | ||
| Programming Language | JavaScript/TypeScript | TypeScript | JavaScript/TypeScript |
| Learning curve | Moderate | Steep | Easy |
| Community Support | Large | Large | Large |
| Performance | High | High | High |
| Scalability | High | High | High |
| Component Architecture | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| CLI Tools | Create React App | Angular CLI | Vue CLI |
| Data Binding | One-way | Two-way | One-way |
| Routing | React Router | Angular Router | Vue Router |
| State Management | Redux, MobX, Zustand, Context API | RxJS, NgRx, Akita | Vuex, Pinia |
| SSR (Server-Side Rendering) | Next.js, Remix, Razzle | Angular Universal | Nuxt.js, Quasar |
| Mobile Development | React Native | Ionic, NativeScript | Vue Native, Quasar |
| UI Component Libraries | Material-UI, Ant Design, Chakra | Angular Material, Clarity | Vuetify, Quasar, Element |
| Job Market Demand | High | Moderate | Moderate |
Please note that the information provided in this table is an approximation and subject to change over time. It is always a good idea to keep up to date with the latest developments in these frameworks, as features and popularity may evolve.
Detailed comparison: React vs Angular vs Vue
Rendering performance
React: React is renowned for its virtual DOM, which enables it to efficiently update and render components by comparing the changes with the actual DOM. This results in excellent rendering performance, particularly in large-scale applications. Additionally, React incorporates concurrent rendering, which further optimizes the rendering process by prioritizing updates based on their importance.
Angular: Angular utilizes a real DOM and leverages ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation and change detection mechanisms to optimize rendering performance. These features, combined with zone.js for efficient change detection, have significantly improved Angular's performance over time. However, it can still struggle with complex applications, particularly when dealing with frequent DOM updates.
Vue: Vue amalgamates the best of both worlds by using a virtual DOM for efficient updates and reactive data binding for quick DOM manipulations. Its lightweight nature makes it particularly performant in smaller applications, but it scales well to larger projects too. Vue 3 introduced the Composition API, which further improves performance by facilitating more granular control over-reactivity and optimization.
Learning curve
React: React has a moderate learning curve due to its unique JSX syntax and functional programming concepts, such as hooks and higher-order components. However, the vast community support, extensive documentation, and popularity in the industry make it easier to find resources and learn quickly. React's flexibility also allows developers to adopt different patterns and architectures based on their preferences.
Angular: Angular has a steeper learning curve, especially for beginners, as it involves understanding concepts like dependency injection, decorators, and TypeScript. Its comprehensive nature as a complete framework might require more time to become proficient. However, Angular's strict structure and best practices can help developers maintain a consistent codebase in large projects.
Vue: Vue is known for its gentle learning curve, with an approachable API and clear documentation. It allows developers to integrate with existing projects incrementally and offers a smooth transition to a fully-featured framework. Its template syntax is familiar to developers with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript experience, making it more accessible to newcomers.
Tooling and ecosystem
React: React boasts a mature and extensive ecosystem, with a wide array of libraries and tools available for every need. Examples include Redux and MobX for state management, React Router and Reach Router for navigation, and Create React App and Next.js for project scaffolding. Additionally, React has a large and active community that consistently contributes to the growth and improvement of the ecosystem.
Angular: Angular's ecosystem is built around its CLI tool (Angular CLI) and includes built-in solutions for routing, forms, and HTTP requests. The Angular community has developed numerous component libraries and tools, such as Angular Material for UI components, Angular Universal for server-side rendering, and Nrwl Nx for monorepo development. Angular's robust ecosystem offers a cohesive experience for developers.
Vue: Vue's ecosystem is growing rapidly, with the official Vue CLI, Vue Router, Vuex for state management, ViteJS for build tooling. There are also several popular component libraries like Vuetify, Quasar, and Element. While Vue's ecosystem may not be as extensive as React's, it is continually expanding and improving. The Vue community is also known for its welcoming and supportive atmosphere.
API stability
React: React's API has remained relatively stable over the years, with Facebook's commitment to providing smooth migration paths for major updates. Backward compatibility is a priority, minimizing breaking changes for developers. The introduction of hooks in React 16.8 was a significant addition, but it was designed to be fully compatible with existing class components.
Angular: Angular has experienced more significant API changes since its inception, particularly with the transition from AngularJS to Angular 2. However, Google has since adopted a predictable release schedule with clear update guidelines, ensuring more stability for developers. Angular now follows semantic versioning, which makes it easier to understand the scope of changes between versions and reduces the risk of breaking changes.
Vue: Vue has maintained a stable API throughout its development, with only minor breaking changes between major versions. The Vue team prioritizes backward compatibility and provides detailed migration guides when necessary. The transition from Vue 2 to Vue 3, for example, was accompanied by a dedicated migration build to help developers identify and address compatibility issues.
Real-world use cases and industry adoption
React: React is widely adopted by large corporations and startups alike, including Facebook, Instagram, Airbnb, and Netflix. Its versatility and performance make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from social media platforms to e-commerce websites, enterprise-level solutions, and even virtual reality experiences with React VR.
Angular: Angular has a strong presence in enterprise environments, with companies like Google, Microsoft, IBM, and Forbes utilizing the framework for their applications. Its comprehensive feature set and built-in tooling make it ideal for complex, large-scale applications and enterprise-level solutions. Angular is also commonly used in financial services, healthcare, and government projects, where its robustness and scalability are highly valued.
Vue: Vue has seen increasing adoption in various industries, with companies like Alibaba, Xiaomi, and GitLab using it for their projects. Its ease of use and flexibility make it suitable for both small and large-scale applications, ranging from single-page applications to advanced web applications and progressive web apps. Vue's growing popularity has also led to its adoption in open-source projects and community-driven initiatives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, React, Angular, and Vue each have their strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of framework ultimately depends on your project's specific requirements and your personal preferences as a developer. React excels in performance, scalability, and community support, making it a go-to choice for many developers. Angular is a comprehensive framework with powerful built-in tooling, making it a favorite among enterprise-level applications. Vue, on the other hand, offers a gentle learning curve and flexible approach, making it an attractive option for both beginners and experienced developers. By understanding the differences and unique aspects of each framework, you can make an informed decision and select the best tool for your next web development project.

